openCV installation guide for Windows
A simple documentation for installing OpenCV on a Windows device without involving third-party tools:
OpenCV Overview:
OpenCV stands for Open Source Computer Vision Library. It is a powerful and widely-used open-source computer vision and machine learning library designed to provide a common infrastructure for computer vision applications. OpenCV is written in C++ and has bindings for various programming languages, including Python, Java, and more.
Usage:
OpenCV is used for a wide range of computer vision tasks and applications. Its key features include image and video processing, object detection and tracking, machine learning, and camera calibration. OpenCV provides a comprehensive set of tools and functions that make it suitable for both academic research and commercial applications.
Applications:
Image and Video Processing: OpenCV is extensively used for basic to advanced image and video processing tasks. It includes functions for image manipulation, filtering, and transformation, as well as video analysis and processing.
Object Detection and Tracking: OpenCV supports various algorithms for object detection and tracking, including Haar cascades, HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients), and deep learning-based approaches. It finds applications in surveillance, robotics, and automated systems.
Machine Learning: OpenCV integrates with machine learning frameworks and tools. It supports techniques like support vector machines (SVM), k-nearest neighbours (KNN), and neural networks. OpenCV's machine learning capabilities are crucial for developing computer vision applications.
Camera Calibration: OpenCV provides tools for camera calibration, which is essential for correcting distortions and obtaining accurate measurements from images. It's widely used in computer vision projects involving cameras and sensors.
Augmented Reality (AR): OpenCV is utilized in AR applications for marker detection, camera pose estimation, and overlaying virtual objects in the real world.
In summary, OpenCV is a fundamental tool in the field of computer vision, offering a rich set of functionalities for image and video processing. Its applications extend across various domains, and its integration with machine learning tools enhances its capabilities in solving complex real-world problems.
Installing OpenCV on Windows:
Step 1: Install Python
If you don't have Python installed, download and install the latest version from the official Python website:
https://www.python.org/downloads/
NOTE - During installation, make sure to check the box that says "Add Python to PATH."
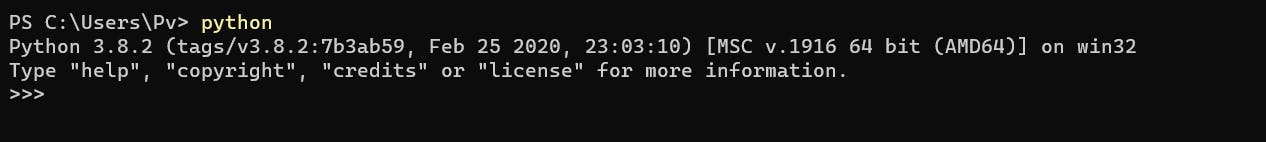
Upon writing python , you'll be shown the version installed as shown below -
Step 2: Open Command Prompt
Open your command prompt by searching for "cmd" in the Start menu or use Windows Powershell.
NOTE - Advised to run as administrator.
Step 3: Run the following commands
Upgrade your pip package (not necessary but advised) by running the following command -
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install --upgrade pip setuptools
Then run - (It is a dependency hence required)
pip install numpy
Now install openCV - https://pypi.org/project/opencv-python/ (For custom Wheel file )
pip install --no-cache-dir opencv-python
Step 4: Verification
To verify Create a simple Python script to verify that OpenCV is installed correctly. Open a text editor, paste the following code, and save it as verify_opencv.py:
import cv2
print("OpenCV version:", cv2.__version__)
image = cv2.imread("path_to_image.jpg")
cv2.imshow("OpenCV Image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Replace "path_to_image.jpg" with the path to an image file on your computer.
Open a command prompt, navigate to the directory containing verify_opencv.py, and run the script:
python verify_opencv.py
If OpenCV is installed correctly, the script will display the OpenCV version and show the image.
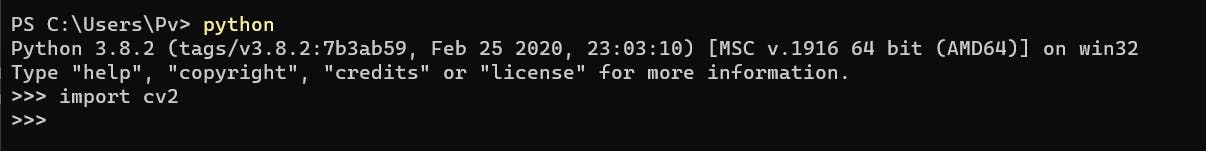
Also, if you import cv, you will not get any error, as shown below -
You have successfully installed OpenCV on your Windows device. This minimalistic approach ensures a clean and straightforward installation without involving third-party tools.